
Evidence for a World in Transition
In 2016, Mathematica extended the reach of our mission to improve public well-being by conducting rigorous research and producing evidence about policies, programs, and populations across our ever-changing world. Here we present brief videos, interactive data visualizations, and other highlights of key areas of our work in the past year. We invite you to watch, click, and read to learn more about research that will have an impact on society in the years to come.
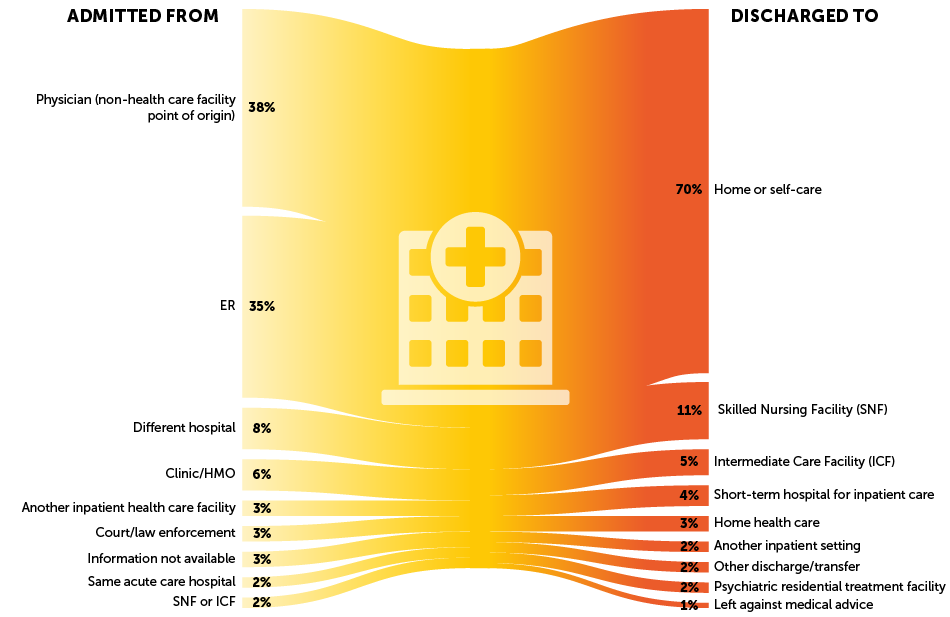
One in five Americans experiences mental illness in a given year. For Medicare beneficiaries with complex health conditions, the transition from a psychiatric care setting back to the community can be particularly challenging. As part of our ongoing commitment to improving the quality of behavioral health care, Mathematica worked with the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), to investigate the trajectory of care among Medicare beneficiaries before and after discharge from inpatient psychiatric facilities. The majority of Medicare beneficiaries who receive inpatient psychiatric care are discharged to home and would benefit from follow-up behavioral health care. However, only 37% have a visit with a mental health practitioner within 30 days of their inpatient psychiatric stay. These findings highlight the need for state agencies, hospitals, health plans, and community providers to work together to improve follow-up care for this population.
Every year, more than two million workers in the United States lose their jobs or leave the workforce because of a medical condition. Only a few states have adopted promising early interventions designed to help some of these workers keep their jobs during a health transition. Working with the U.S. Department of Labor, Mathematica has identified opportunities for states to intervene early to improve job retention for diverse target populations.

Children whose caregivers misuse alcohol or drugs or have substance use disorders may experience wide-ranging adversity, including out-of-home placements. With congressional funding, the Children’s Bureau within the Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Administration for Children and Families at HHS, established the Regional Partnership Grant (RPG) program to improve the well-being, permanency, and safety outcomes of such children and their families. RPG grants fund evidence-based and evidence-informed programs and services that seek to prevent the placement of at-risk children into out-of-home care. Mathematica is leading the cross-site evaluation of the RPG program.

Transitions to elementary, middle, and high school provide an opportunity for parents to search for new schools in ways that have major implications for diversity and equity. In research supported by the Walton Family Foundation, Mathematica explored how parents' rankings of school alternatives can be used to simulate the effects of different policies related to school choice.
Using data from the District of Columbia, the researchers found that DC's current open-enrollment system, which assigns students by lotteries if schools are oversubscribed, may slightly improve or worsen segregation compared with assigning students to their neighborhood school—depending on whether we look at elementary, middle, or high school or whether we consider segregation by race or income. But if popular schools could be expanded to allow more students to enroll, not only would more people get their first choice, but the overall levels of segregation by race and class would be lower than with either neighborhood schools or the current policy.
In work for the Employment and Training Administration in the U.S. Department of Labor, Mathematica and its partners conducted a rigorous national evaluation of staff assistance, also called "intensive services," and training provided through two of the nation's largest publicly funded employment and training programs, the Adult and Dislocated Worker programs. Using data from the first 15 months after study enrollment, Mathematica researchers found that access to intensive services led to higher employment rates and higher earnings. The researchers are currently examining data on the 30 months after study enrollment to determine whether these findings persist and if training was effective.
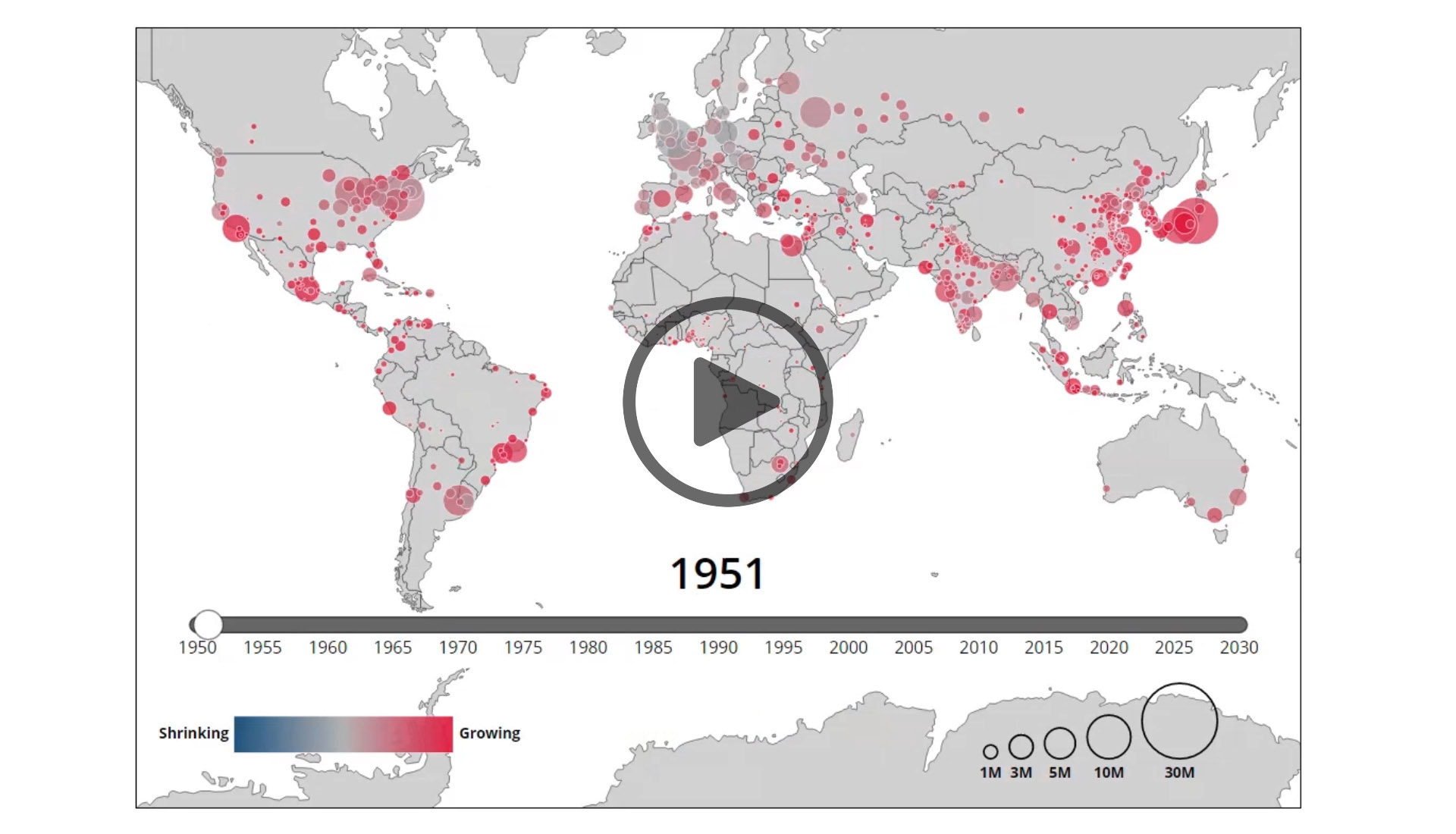
In 2010, for the first time in history, more than half of the world's population lived in an urban area. By 2030, it is predicted that five billion of the world's eight billion inhabitants will live in cities, with significant urban growth predicted in Africa, China, and South Asia. This transition to increased urbanization will have long-term global implications for climate change and the environment. Mathematica looks forward to continuing our partnership with the Children's Investment Fund Foundation, the C40 Climate Leadership Group, and other organizations seeking to test, measure, and implement effective strategies for decreasing global greenhouse gas emissions.
Moving low-income workers into promising jobs is essential for transitioning many families from welfare to self-sufficiency. This is the goal of Project AWESOME: Advancing Welfare and Family Self-Sufficiency Research, conducted by Mathematica on behalf of HHS’s Administration for Children and Families, Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation. For this project, Mathematica identified promising occupations in all 50 states that are achievable for low-income workers after a relatively short-term investment in education or training. Project AWESOME is producing cross-cutting research that advances the field of family self-sufficiency and stability research.
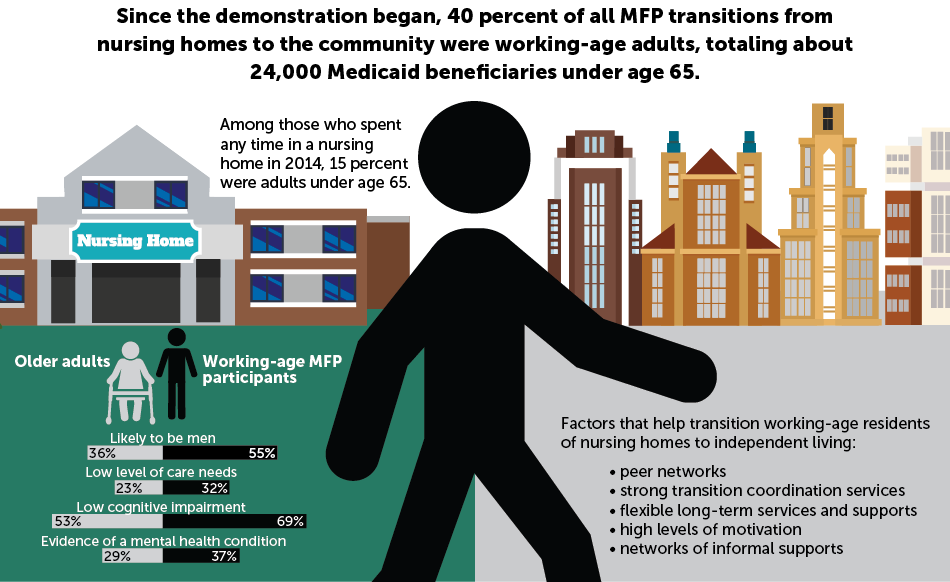
Many people living in long-term care facilities can and want to live in community-based settings. With the right supports, these long-term care residents can transition successfully to community settings. In work for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Mathematica is assessing the effects of the Money Follows the Person Demonstration, a $4 billion effort to transition long-term care residents back to the community, with services and supports “following the person” to his or her chosen location. Our research indicates that working-age adults are a growing share of nursing home residents and that, compared with their older counterparts, working-age residents have low levels of care needs—suggesting that with good social support and housing, they can make the transition to community living.
Many girls in Burkina Faso do not complete primary education, limiting their choices as adults as well as their opportunities for economic and social well-being. To improve girls' transitions into adulthood through education, the government of Burkina Faso launched "Burkinabé Response to Improve Girls' Chances to Succeed," or BRIGHT, in 132 villages throughout the country, where rates of primary school enrollment were the lowest nationwide. Starting in 2005, BRIGHT funded the construction of primary schools, one in each village, and implemented a set of complementary interventions. Supported by the Millennium Challenge Corporation, Mathematica evaluated BRIGHT's 10-year impact on enrollment, attendance, test scores, and young adult outcomes.

The nutritional quality of the food that children eat matters—for their health and their learning. Since the early 1990s, Mathematica researchers have studied school meals to help improve school nutrition policies. A recent examination reveals how the findings from the School Nutrition Dietary Assessment (SNDA) studies, conducted for the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Food and Nutrition Service, influenced the evolution of school nutrition policy over the past two decades. The SNDA studies were designed to monitor the nutritional quality of school meals and trends in their composition between school years 1991–1992 and 2009–2010. Our analysis specifically highlighted the influence of changing requirements for milk as a result of data-driven policy transitions over time.
For more information about the studies featured here and our other work,
please visit:
www.mathematica-mpr.com or contact us at press@mathematica-mpr.com.
